Installing and Setting Up Aruba Central (on-premises)
Aruba Central (on-premises) combines industry-leading functionality with
an intuitive user interface for easy monitoring and management of your wired and wireless networks. It scales to support
three to five node clusters with up to 8,000 to 16,000 devices, or seven node clusters
This document helps you plan for and complete the installation of Aruba Central on a physical appliance, or your multi-node Aruba Central clusters.
Before You Begin
The following information will help you configure the Aruba Central servers and prepare your deployment.
IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS
Ensure the below details are ready before setting up Aruba Central (on-premises). Ensure that the following are correct and are reachable.
|
|
Any mistype or incorrect details in the Network settings cannot be reverted. The only option is to reinstall Aruba Central (on-premises). |
FQDNFully Qualified Domain Name. FQDN is a complete domain name that identifies a computer or host on the Internet., IP Address, SubnetSubnet is the logical division of an IP network. Mask, Gateway, DNSDomain Name System. A DNS server functions as a phone book for the intranet and Internet users. It converts human-readable computer host names into IP addresses and IP addresses into host names. It stores several records for a domain name such as an address 'A' record, name server (NS), and mail exchanger (MX) records. The Address 'A' record is the most important record that is stored in a DNS server, because it provides the required IP address for a network peripheral or element. IP for each node in cluster
VIP (Virtual IP for cluster), Subnet Mask, Gateway and FQDN (FQDN for VIP) for cluster.
|
|
The Aruba Central appliance opens multiple ports for communication, so it is recommended that you host the Aruba Central appliance behind a firewallFirewall is a network security system used for preventing unauthorized access to or from a private network.. The APIApplication Programming Interface. Refers to a set of functions, procedures, protocols, and tools that enable users to build application software. Gateway that is created as apigw-<clusterfqdn> resolves to the same cluster IP address. |
Prerequisites
To complete the Aruba Central setup, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
Console access to the Aruba Central (on-premises) appliances, either hardware or virtual via HPE Integrated Lights Out connection.
Server’s iLO port is connected to a switch that has DHCPDynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A network protocol that enables a server to automatically assign an IP address to an IP-enabled device from a defined range of numbers configured for a given network. and Gateway IP, which are reachable to setup the server. The iLO credentials are placed on the top of the server. Ensure to make a note of the iLO credentials. These credentials are needed to access the server using iLO. Configure the server to RAID 0.
A valid FQDN for each Aruba Central (on-premises) server node, which resolves with the IP address you configure in the network settings during Aruba Central setup. These FQDN should be resolvable by any client that you will log into Aruba Central (on-premises) with. That is, by devices that are monitored or managed by Aruba Central (on-premises), and by all Aruba Central (on-premises) nodes.
If you are using APIs, ensure that the API Gateway FQDN resolves with the same cluster IP address as the Aruba Central server if you use OAuthOpen Standard for Authorization. OAuth is a token-based authorization standard that allows websites or third-party applications to access user information, without exposing the user credentials. 2.0 to access the Aruba Central APIs.
Firmware Versions
Following are the recommended Firmware versions to install Aruba Central (on-premises):
BIOS version - 2.34
iLO version – 1.46
RAID controller – 3.00
HDD - configured with RAID-0
Supported Ports
Configure the appropriate ports. Following table lists the supported ports:
| Protocol and port | Domain Names and Purpose |
|---|---|
|
To access pool.ntp.org for updating internal clock on APs. |
|
|
To access device.arubanetworks.com for getting a provisioning rule from Aruba Activate. Devices such as APs must be able to resolve device.arubanetworks.com using a valid DNS server. |
|
|
To access activate.arubanetworks.com and configure provisioning rules in Aruba Activate. |
|
|
To access rcs-m.central.arubanetworks.com and establish a connection with the AP console through SSHSecure Shell. SSH is a network protocol that provides secure access to a remote device. . |
|
|
To access aruba.brightcloud.com (BrightCloud WebCC server) for website content classification. |
|
|
To access coreupdate.central.arubanetworks.com and allow Aruba Central to check firmware versions for automatic upgrades. |
|
|
To access images from the quay.io registry. |
|
|
To access and manage Aruba Central (on-premises). |
|
|
To access the outbound internet access. |
|
|
For HTTPSHypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. HTTPS is a variant of the HTTP that adds a layer of security on the data in transit through a secure socket layer or transport layer security protocol connection. and websocket between Aruba Central (on-premises) and devices. |
|
|
UDP 8211, 8285 |
To receive AMONAdvanced Monitoring. AMON is used in Aruba WLAN deployments for improved network management, monitoring and diagnostic capabilities. messages and view data for controllers in the Aruba Central monitoring dashboard. |
|
TCP 22 |
For management access through SSH and cluster setup. |
|
For CLI between Aruba Central (on-premises) and devices. |
|
|
TCP 80 |
For browser redirect from HTTPHypertext Transfer Protocol. The HTTP is an application protocol to transfer data over the web. The HTTP protocol defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and the actions that the w servers and browsers should take in response to various commands. to HTTPS. |
|
To upgrade firmware on the devices managed by Aruba Central. |
|
|
To access the outbound internet access. |
|
|
TCP 2379, 2380, 4343, 4433, 6433, and 10250 |
For communication between Aruba Central nodes in a cluster. |
|
Port 4343 |
To access the setup-wizard installation. |
|
TCP 30633 |
To allow the devices to set up a connection with the OpenFlowOpenFlow is an open communications interface between control plane and the forwarding layers of a network. controller. |
|
Port 25, 456, or 587 |
Dependent on the SMTPSimple Mail Transfer Protocol. SMTP is an Internet standard protocol for electronic mail transmission. configuration for alerts, reports, and Aruba Central (on-premises) account registration. |
|
UDP 161, 162 |
Connections to the Server
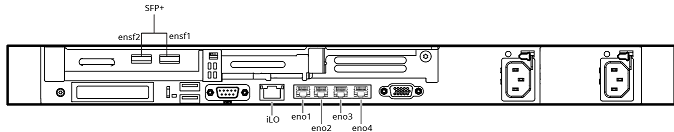
Connect the following cables to the correct ports based on the figure below:
Connect an EthernetEthernet is a network protocol for data transmission over LAN. cable to the iLO port and to the switch which has DHCP IP.
Connect another Ethernet cable to the eno1 port which is the Ethernet port.
Connect a monitor to the VGA port on the server to see the iLO IP Address.
Connect a key board to the server to setup the server.

Once the server is powered on and the cables connected to iLO and eno1, reboot the server using the power button or unplug and plug the power cable. The monitor displays the iLO IP address assigned by the DHCP server.
Installing and Setting Up Central Appliance
The Aruba Central (on-premises) can be installed only on Central-ready Central appliance and not on Central-ready Airwave appliance.
In case of Central-ready Airwave appliance, you must perform the ISO and COP Installation procedures mentioned in Step 1 and Step 2 before setting up the network.
In case of Central-ready Central appliance, jump to Step 3 to set up the network.
During the installation and setup process, the administrator account on the iLO logs out and a new COP iLO user account is created. The BIOS password is secured as an internal hash.
Perform the following steps to set up the Aruba Central (on-premises) in the Central appliance:
Step 1: Perform the ISO Installation
For more information, see ISO Installation.
|
|
Ensure that the server is configured to RAID 0. |
Step 2: Perform the Aruba Central (on-premises) Installation
For more information, see COP Installation.
Step 3: Setting up the Permanent Network
The procedure to set up of permanent network performed for both Central-ready Airwave appliance and Central-ready Central appliance models is mandatory on all the nodes that are a part of Aruba Central (on-premises) cluster. For more information, see Aruba Central (on-premises) Installation Guide-Technotes.
The Central-ready Central appliance is pre-installed with Aruba Central (on-premises). Hence, you are required to set up the server, or the cluster only. For more information, see Aruba Central (on-premises) Installation Guide-Technotes.
Step 4: Run the Network Setup from the CLI
1. Log in to Aruba Central CLI through a serial console.
2. At the prompt, log in to the server using the following credentials:
user name =
password =
|
|
You can derive the serial number from the label of the iLO processor. For example, SGH943Y8KT. Any mistype or incorrect details in the Network settings cannot be reverted. The only option is to reinstall Aruba Central (on-premises). |
Step 5: Configure the Aruba Central server
1. At the prompt, perform the following actions:
a. Enter to select the option and go to the next menu item.
b. Enter to select the option and go to the next menu item.
c. Enter to select the Settings option and go to the next menu item.
2. When prompted, enter the following network settings:
Network Interface
Server IP address
Subnet mask
Gateway IP address
DNS server IP address
Secondary DNS server address (optional)
Following network interfaces are supported:
|
|
Select only one network interface to configure the server. Perform the above mentioned steps for all the nodes, if you are setting up a multiple node cluster. |
3. Enter the host name or FQDN of the Aruba Central server (for example, *company.com).
4. Enter the timezone from the displayed list.
5. Set up the NTPNetwork Time Protocol. NTP is a protocol for synchronizing the clocks of computers over a network. settings
Step 6: Configure the Cluster
To configure the cluster:
1. Log in to the UI using any one of the server IP addresses configured previously with the following credentials:
— https://<serverIP>:4343
—copadmin/chassis serial number>
The setup wizard is displayed.
2. In the tab of the Wizard, select the number of nodes (1, 3, 5 or 7) in the cluster from the drop-down list. Based on your selection, the number of Host Names and IP addresses fields are displayed.

|
|
Aruba Central automatically fills the master Host name and IP address. |
3. Enter the for each node. The IP address gets populated automatically when you enter the host name.
4. Click .
The tab is displayed.

5. In the tab, enter the following network information for each node:
FQDN of the node (for example, *company.com)
Virtual IP address
User name and password for the CLI administrator
User name and password for the GUI administrator.
6. If you want to configure a proxy server, select the option, then enter the following information:
Proxy server host name
Proxy server port
Proxy server user name and password
7. Click .
8. In the tab, click to advance through the setup wizard.
9. In the tab, select the SMTP Server Setup option, then enter the following information:
SMTP server host name or IP address
SMTP port
SMTP user name and password
10. Click .
|
|
The cluster setup may take time depending on the number of nodes. For example, setting up a seven-node cluster may take up to 2 hours. |
After the Aruba Central setup completes, the CLI administrator and GUI administrator accounts are created.

